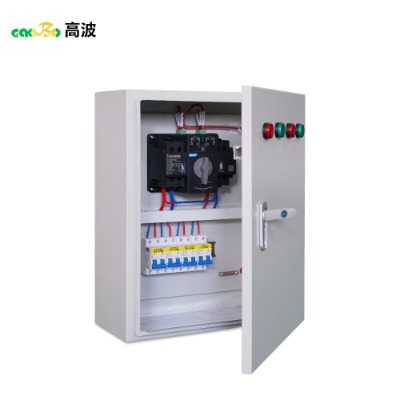
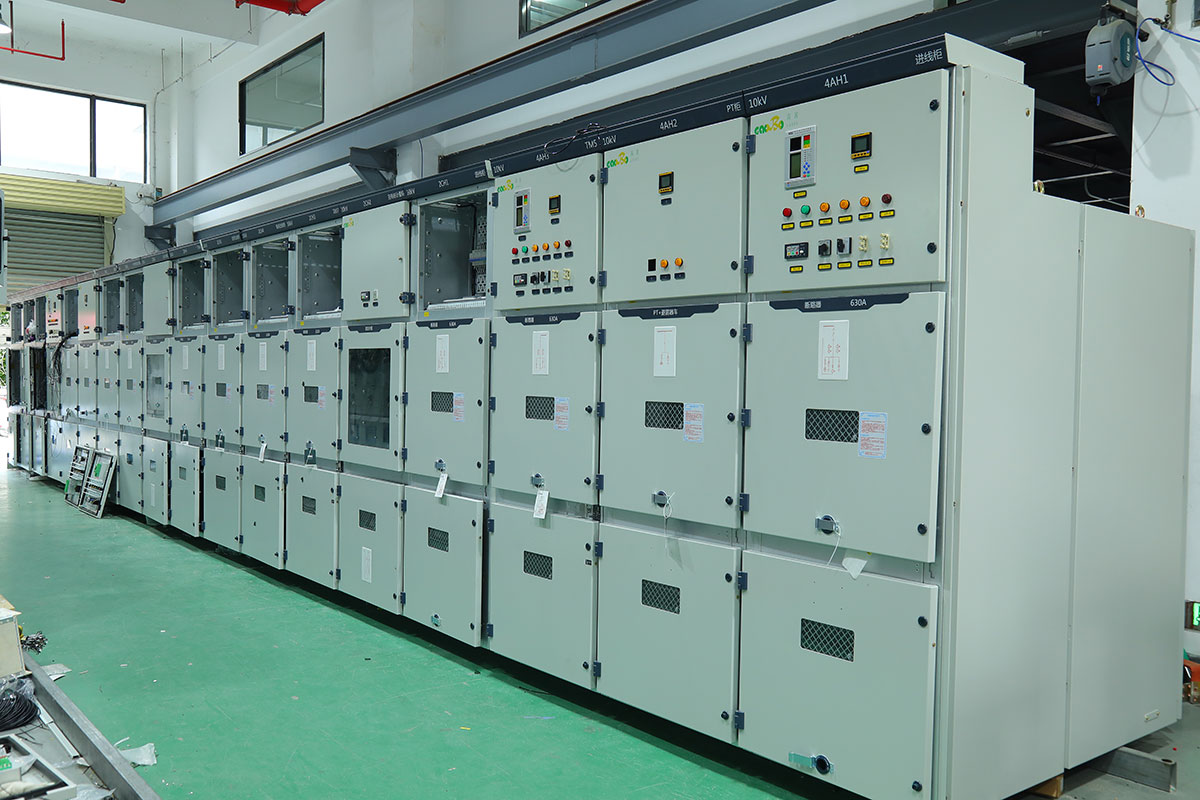
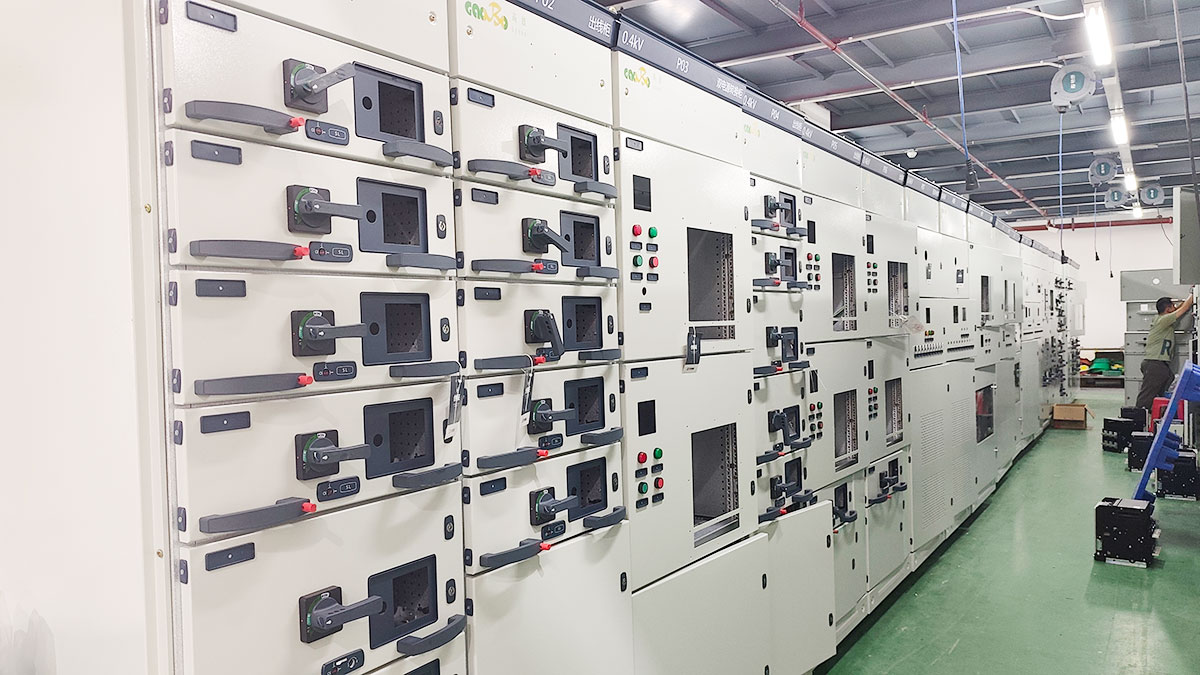
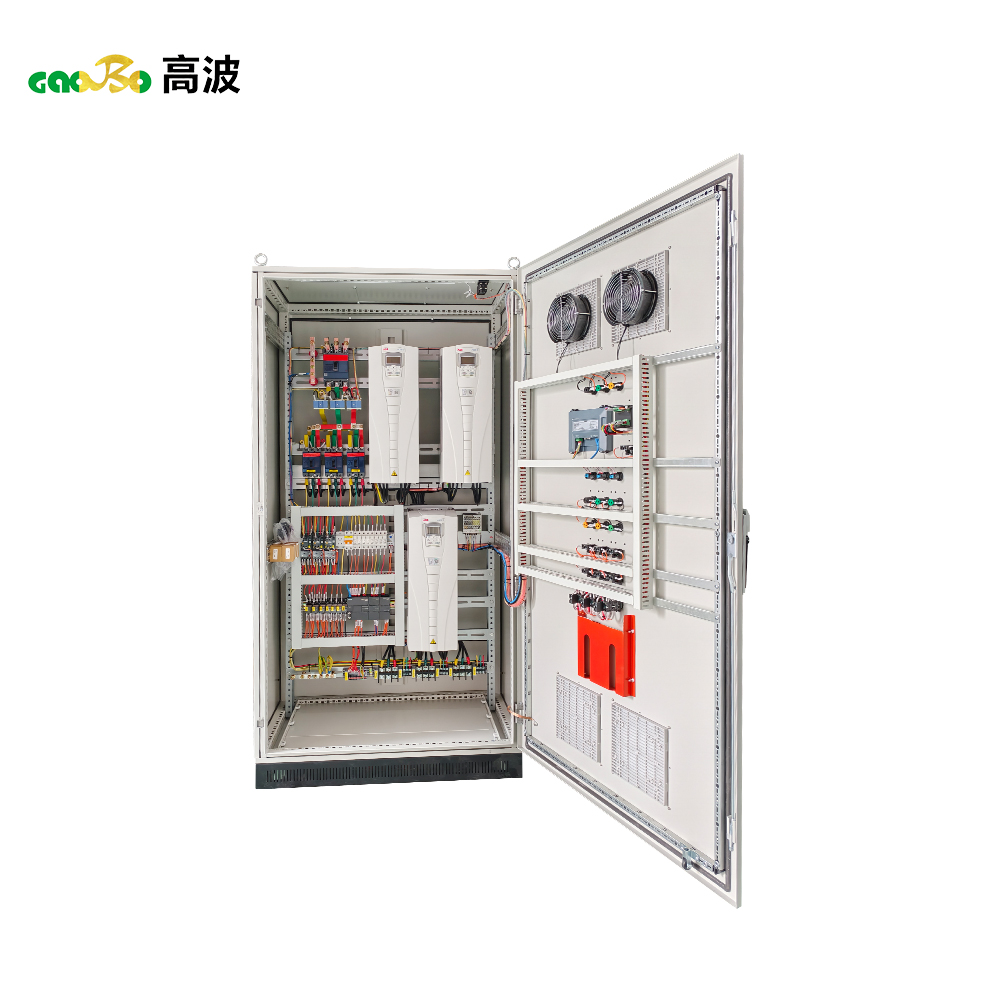
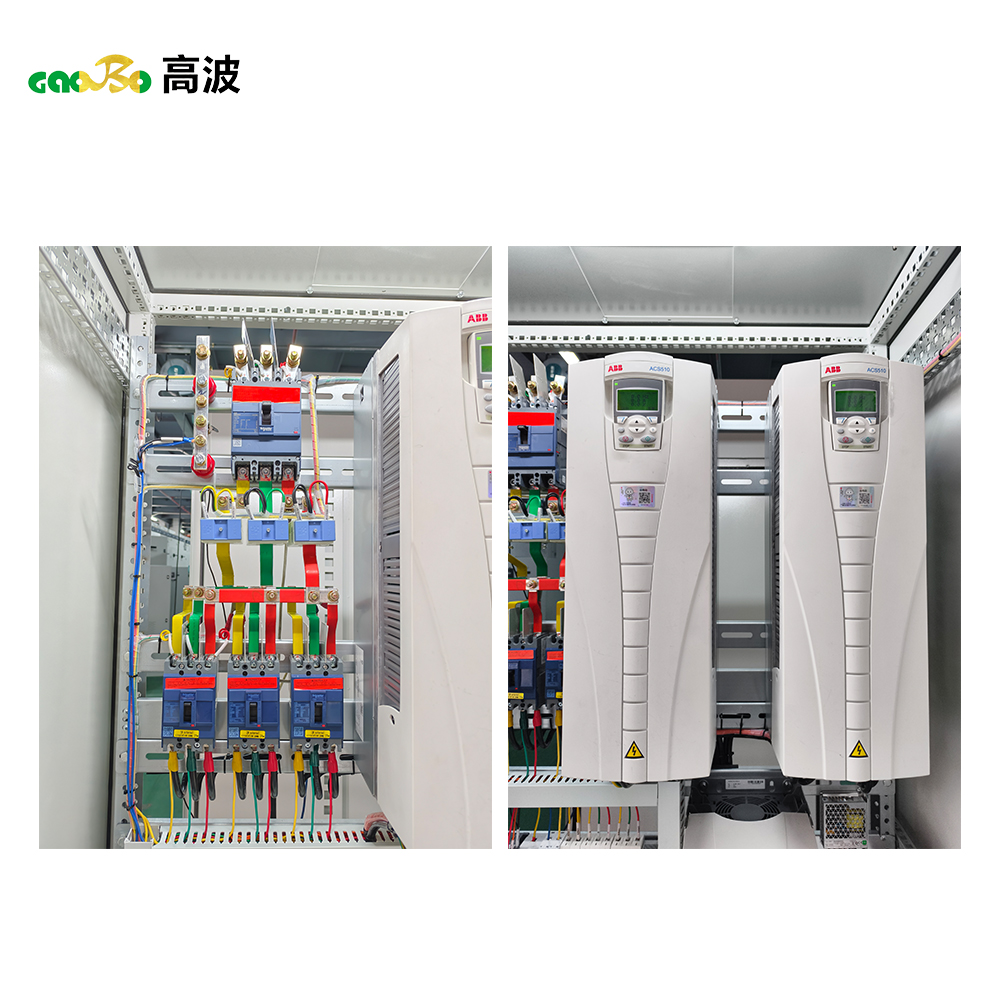
Whats is Box-type Substation?
A box-type substation, abbreviated as "box substation," is internationally known as a "prefabricated substation" or "compact substation." It is a complete set of power distribution equipment that integrates high-voltage switchgear, distribution transformers, low-voltage switchgear, electricity metering equipment, and reactive power compensation devices, all pre-assembled in one or more fully enclosed, moisture-proof, and rust-proof steel structures at the factory according to a specific wiring scheme.
Simply put, it's a "portable mini-substation," achieving the integration and modularization of substation, power distribution, control, protection, and metering functions.
Gaobo Power Solution Factory make high quality Modern Power Distribution System Box-type Substation and offer custom service.
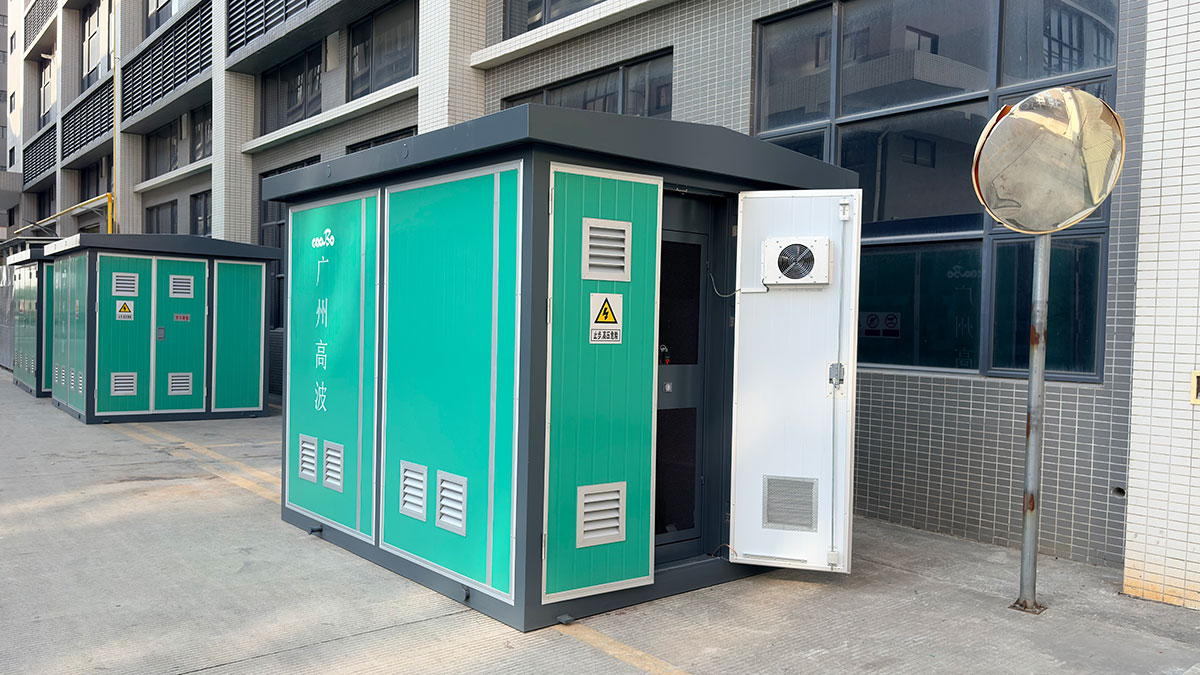

Main Features:
1. Integration and Modularization: All equipment of a traditional civil engineering substation is integrated into one or several connectable modules, resulting in a compact structure and achieving "factory-built substations."
2. Rapid Deployment: After arriving at the site, only positioning the modules, connecting cables, and commissioning are required for operation. The construction period is shortened by more than 60% compared to traditional substations.
3. Fully Enclosed Operation: The modules are made of metal or non-metallic (environmentally friendly) materials, with a fully enclosed design and a protection rating typically reaching IP23-IP54. This effectively prevents dust, moisture, and small animals from entering, making them suitable for harsh outdoor environments.
4. Small footprint: Compared to traditional civil engineering substations, it saves approximately 70%-90% of land area, making it particularly suitable for areas with limited land resources.
5. Aesthetically pleasing and environmentally harmonious: The enclosure can be designed to blend in with the landscape (e.g., with wood grain patterns or covered with greenery), easily integrating into urban or scenic environments.
6. Movable and reusable: When the power load center shifts, the entire substation can be relocated to a new location for continued use, resulting in a high return on investment.
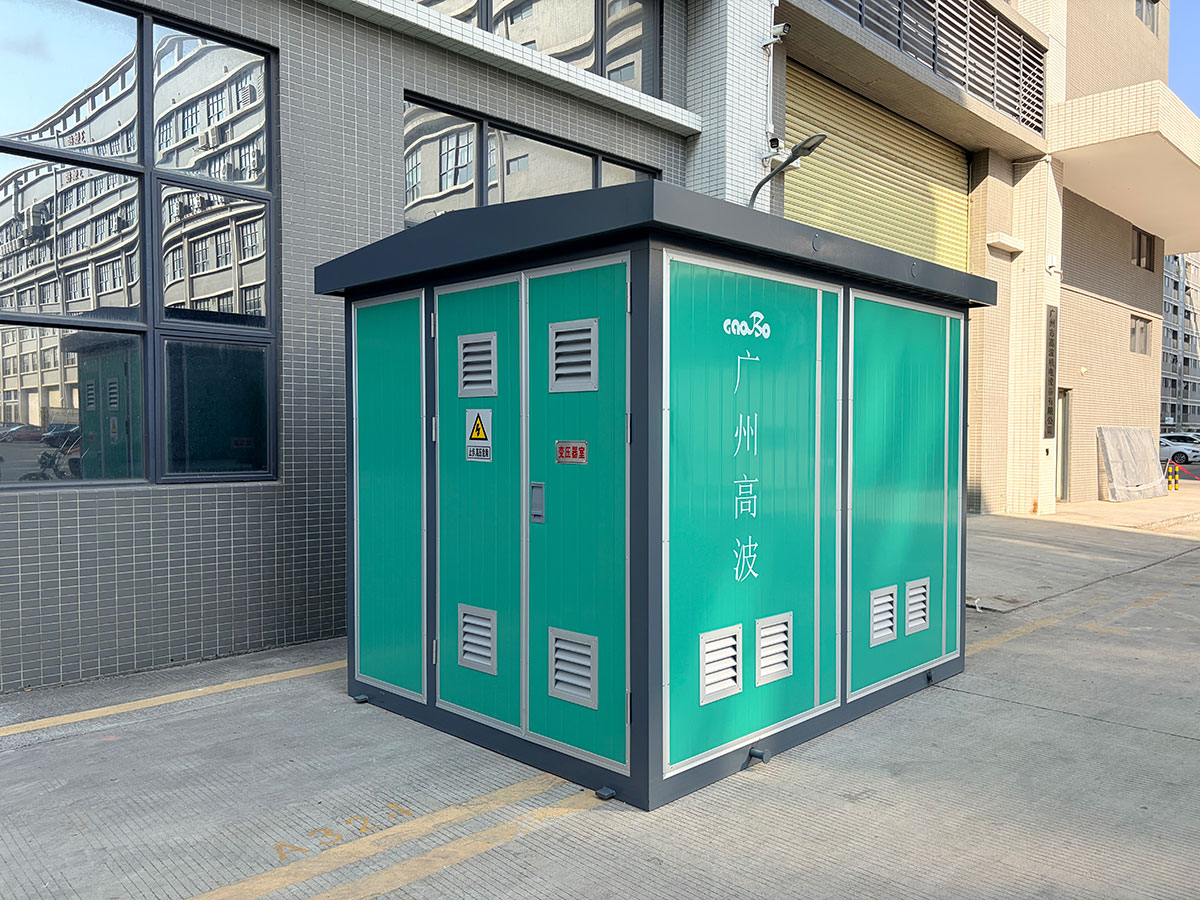

Application:
1. Urban public power distribution: Power grid expansion and end-user power supply for streets, residential areas, commercial centers, and parks.
2. Temporary power supply: Temporary power needs for construction sites, large-scale events, disaster relief, etc.
3. Industrial and mining enterprises: Independent power supply units for workshops or production lines in mines, oil fields, and factories.
4. New energy sector: Used as step-up substations or collection stations for photovoltaic power plants and wind farms.
5. Transportation infrastructure: Distributed power supply points along highways, railways, airports, and port terminals.
6. Rural power grid renovation: Quickly solves the problems of long power supply radius and low voltage quality in rural areas.
Core components and key technical parameters:
| Component |
Major Equipment |
Key Parameters |
| High-Voltage Room |
High-voltage load switch, fuses, surge arresters, live-line indicators |
Rated voltage: 10kV, 35kV
Rated current: 630A
Short-circuit breaking current: 16kA, 20kA
Protection class: IP3X
|
| Transformer Room |
Distribution Transformers (typically dry-type or oil-immersed) |
Rated capacity: 200kVA, 400kVA, 800kVA, 1250kVA
Impedance voltage: Uk% = 4%, 6%
Insulation class: Class F, Class H
|
| Low-voltage switchgear room |
Low-voltage circuit breakers, metering instruments, capacitor compensation devices, intelligent monitoring units |
Rated voltage: 0.4kV
Rated current of main circuit: up to 4000A
Compensation capacity: Configured at 20%-40% of the transformer capacity
|
| Enclosure Structure |
Steel frame, sandwich panels (with insulation), ventilation and cooling system | Shell Material: Color-coated steel, stainless steel, aluminum, non-metallic (GRC/SMC) |
Enclosure material: Color-coated steel, stainless steel, aluminum plate, non-metallic (GRC/SMC)
Protection rating: IP23D, IP54
Corrosion resistance rating: C4 or higher
|
Major Advantage:
1. High investment efficiency: Significant savings in civil engineering, design, and installation costs, resulting in an overall cost reduction of approximately 30%-50%.
2. Extremely short construction period: From ordering to commissioning, it only takes a few weeks to one month, greatly accelerating the power supply process.
3. High Safety and Reliability:
Five-way interlocking: Equipped with a complete mechanical or electrical interlocking system to prevent misoperation.
Fully insulated/semi-insulated: The high-voltage section can adopt a fully insulated enclosed structure to reduce the risk of electric shock.
Intelligent monitoring: Optional online monitoring systems for temperature, humidity, smoke, and access control are available for unattended operation.
4. Environmentally friendly and aesthetically pleasing: Factory production reduces on-site pollution and noise; flexible design minimizes disruption to the urban landscape.
5. Easy maintenance: Each unit is independent, and maintenance work does not interfere with other units. The intelligent monitoring system enables remote fault diagnosis and status monitoring.
6. High standardization and flexibility: The product series is highly standardized, and customized designs can be provided to meet specific customer needs.

Box-type substations are a typical product of the modern power distribution system's evolution towards miniaturization, intelligence, environmental friendliness, and aesthetic integration. They perfectly address the pain points of traditional substations, such as large footprint, long construction periods, and environmental impact, and are particularly well-suited to the power needs of new urbanization, distributed energy integration, and rapid deployment. With the advancement of the Internet of Things and the pursuit of carbon neutrality goals, intelligent box-type substations integrating more smart sensing, energy efficiency management, and low-carbon technologies will become one of the core nodes of future power distribution networks.