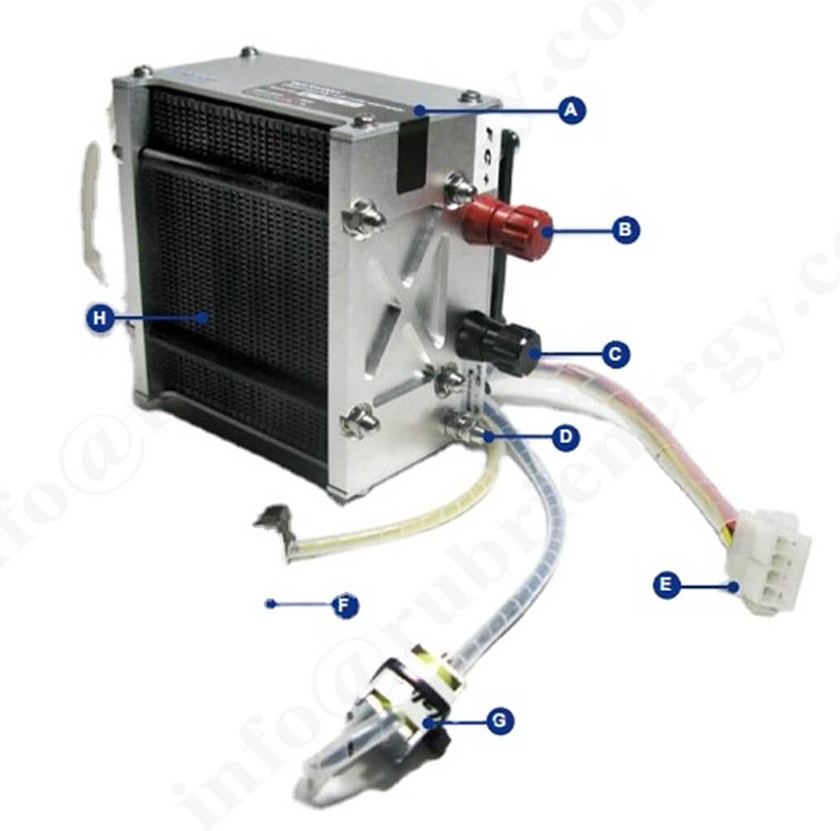
As a core technology in the field of clean energy conversion, hydrogen fuel cells consistently demonstrate near-perfect performance potential in laboratory environments—high efficiency, high power density, excellent start-up characteristics, and stability—making them a "technology star" in the clean energy sector. However, when the technology is scaled up from small-area single cells in the laboratory to real-world applications such as automotive power and distributed power generation, its system efficiency, power output stability, and durability often experience significant degradation, typically ranging from 20% to 50%. This is essentially a concentrated burst of problems from multiple dimensions, including material properties, component integration, and system regulation, when scaled up.

1. Laboratory vs. Real-world: Two drastically different operating environments
The core of laboratory testing for fuel cells is "precise control and interference elimination." Taking the internationally accepted DOE (U.S. Department of Energy) testing protocol as an example, the testing process requires maintaining constant temperature (typically 60-80℃), constant humidity (relative humidity 80%-100%), high-purity reactant gas (hydrogen purity 99.97%, impurity content <10ppm), and stable load conditions. Small-area single-cell batteries (typically <50cm²) are fixed using precision clamps to minimize the impact of external environmental fluctuations on battery performance. Under these ideal conditions, the peak power density of fuel cells can easily reach 400-600mW/cm², and the durability test life can even exceed 10,000 hours.
However, real-world applications are fraught with uncertainty: in automotive powertrains, frequent start-stop cycles, rapid acceleration, and deceleration cause drastic load fluctuations; distributed power generation requires handling diurnal temperature variations, humidity changes, and hydrogen supply of varying purities; even portable devices face random variations in ambient temperature and gas flow conditions. More importantly, the precise temperature and humidity control equipment used in laboratory tests, disregarding energy consumption, must be driven by the fuel cell itself in real-world systems, further compressing the effective output power.
2. Dynamic Deactivation Mechanism of Catalysts
On the one hand, frequent start-stop cycles and load changes in applications cause drastic fluctuations in the cathode potential between 0.4 and 1.0 V. This potential cycling accelerates the dissolution-redeposition process of platinum (Pt) nanoparticles, leading to particle coarsening and electrochemical corrosion of the carbon support, ultimately causing catalyst particle detachment. Accelerated stress test data from the USDRIVE Consortium in the United States shows that in tests simulating 100,000 km of passenger vehicle driving conditions, the active surface area of the Pt catalyst decreased by 42% within 1000 hours, while in laboratory steady-state tests, the loss rate within the same time period was only 8%.
On the other hand, impurity gases in real-world scenarios exacerbate catalyst poisoning. The high-purity hydrogen (impurities <10ppm) and clean air used in laboratory tests are difficult to guarantee in real-world scenarios. Industrial byproduct hydrogen may contain impurities such as CO (often >50ppm) and H2S, while pollutants like SOx and NOx from the air will also enter the battery with the intake air. These impurities will irreversibly adsorb onto the Pt active sites, forming a dense adsorption layer that blocks the reaction. For example, the adsorption energy of CO and Pt is as high as -60kJ/mol; even long-term accumulation of ppb-level CO will lead to a significant decrease in catalyst activity. Test data from Toyota Motor Corporation in Japan shows that when the CO content in the hydrogen reaches 20ppm, the fuel cell output power decreases by 20% within 200 hours; if the CO content increases to 50ppm, the power decrease can reach 45% within the same time period.
In actual operation, changes in fuel cell load are accompanied by fluctuations in the amount of water produced in the reaction, causing the proton exchange membrane to repeatedly undergo the "water absorption and expansion - water loss and contraction" process, generating continuous mechanical stress, ultimately leading to membrane crack propagation and perforation. Research data from the Max Planck Institute in Germany shows that in dynamic humidity cycling tests simulating automotive conditions, the tensile strength of perfluorinated proton exchange membranes decreased by 30% after 500 cycles, and significant cracks appeared after 1000 cycles. Simultaneously, during fuel cell operation, low-potential, high-oxygen-concentration regions generate hydroxyl radicals (.OH). These strong oxidizing substances attack the polymer backbone of the membrane, leading to a decrease in molecular weight, damage to the ion cluster structure, and ultimately, loss of proton conductivity. Tests show that the fluoride ion release rate of the perfluorinated membrane under dynamic conditions reaches 1.2 pg/(cm²·h), which is 12 times that under laboratory constant humidity conditions (0.1 pg/(cm²·h)). The large release of fluoride ions directly reflects the degree of membrane structure degradation.
4. The Superposition of Inhomogeneity and System losses:
Expanding the battery area from laboratory level (<50 cm²) to commercial level (>200 cm²) leads to significant inhomogeneities in internal gas distribution, current density, and temperature distribution, significantly accelerating material degradation. More problematic is the amplification of the "weakest link effect" when hundreds of cells are connected in series to form a stack. This means that a performance degradation in any single cell can drag down the entire stack, leading to a significant reduction in power and lifespan. Test data from General Motors in the US shows that in a stack composed of 200 cells, if the individual cell consistency deviation increases from 3% to 8%, the overall output power of the stack decreases by 22%, and its lifespan is shortened by 35%.
System integration introduces efficiency losses and dynamic response lag. In actual operation, the Balance of Production (BOP) system, which provides air, humidity, and cooling to the stack, consumes a significant amount of energy, potentially lowering the system's net efficiency from over 55% in the laboratory to around 40%. Simultaneously, under dynamic conditions such as rapid vehicle acceleration or start-stop, the response speed of these auxiliary systems lags far behind changes in power demand, resulting in instantaneous power drops and exacerbating damage to critical components such as the proton exchange membrane, thus accelerating the overall system performance degradation. Real-world data from the Toyota Mirai fuel cell vehicle confirms this phenomenon: its stack's peak efficiency is 58%, but the net efficiency of the entire power system is only 42%, with the core difference lying in the losses of the auxiliary systems.
5. From Operating Condition Simulation to Integrated Design
Crossing the performance gap between the "laboratory" and "real-world" environments requires collaborative breakthroughs in three dimensions: testing methods, structural design, and system integration.
First, establishing a testing system that closely reflects actual dynamic operating conditions. Building upon steady-state testing, dynamic testing standards with environmental variables and load cycles need to be introduced. By replicating real-world operating conditions, the fragility of materials and components can be exposed in advance, reducing the discrepancy between laboratory and real-world data.
Second, optimizing the structure and materials of large-area batteries. To address the inhomogeneity issues after scaling up, gradient electrodes and biomimetic flow channels can be applied to reduce current density deviations. Simultaneously, key materials such as highly stable catalysts and self-healing proton exchange membranes can be developed to improve durability from the source.
Third, promoting integrated system design. Energy consumption can be reduced by optimizing the structural design of auxiliary systems.
Future and Outlook:
Fuel cell technology is continuously bridging the gap between the "laboratory" and "real-world applications" through multidisciplinary collaborative innovation. With a deeper understanding of hydrogen fuel cell systems, researchers are able to more accurately predict large-scale battery performance and optimize stack design structures, thereby accelerating the maturation and large-scale application of this clean energy technology.